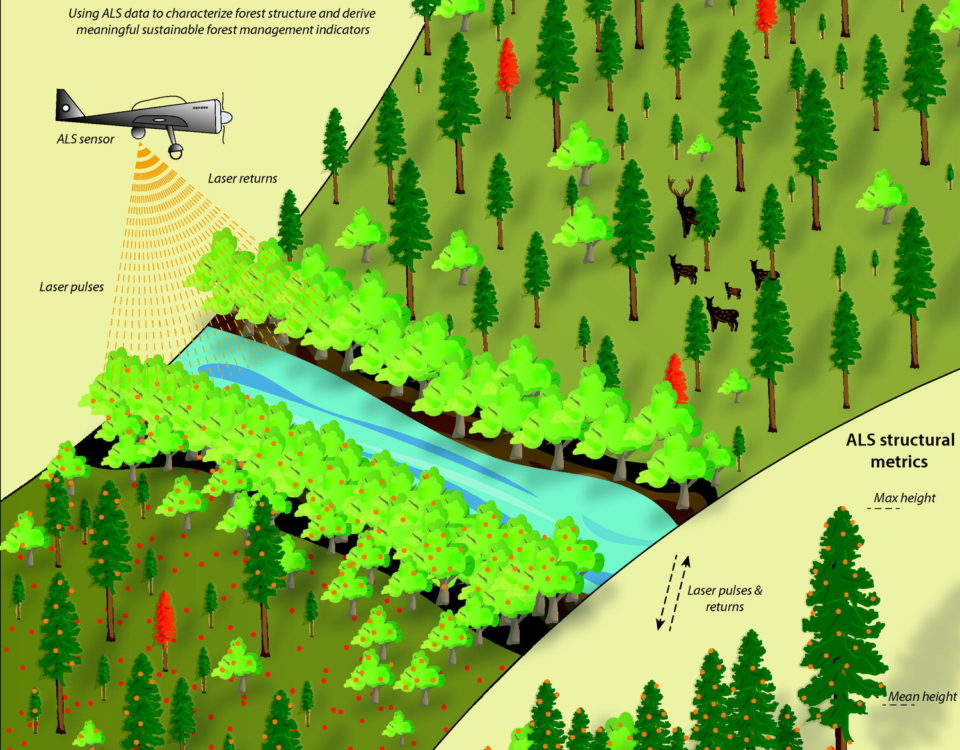
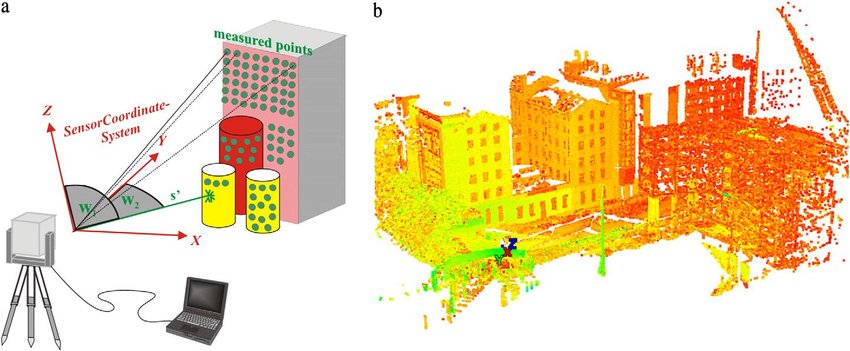
In the realm of land surveying and geospatial data collection, technology has been evolving rapidly over the past few decades. Traditional surveying methods have been the cornerstone of land development and construction projects for centuries, but the advent of laser scanning technology has introduced a new dimension to the field. In this blog, we will compare the strengths and weaknesses of laser scanning technology against traditional surveying methods, helping readers understand when to use each approach.
Traditional Surveying Methods
Traditional surveying methods involve the use of manual instruments such as theodolites, total stations, and leveling equipment to measure angles, distances, and elevations on the ground. This approach relies heavily on human skill and precision and has been a trusted method for generations. Let’s delve into the pros and cons of traditional surveying.
Pros of Traditional Surveying:
- Accuracy: Skilled surveyors can achieve a high level of accuracy when measuring angles, distances, and elevations using traditional instruments.
- Cost-Effective for Small-Scale Projects: Traditional surveying methods are often more cost-effective for small-scale projects with limited surveying requirements.
- Suitable for Rough Terrain: In challenging terrains where laser scanning may be difficult, traditional surveying can still provide reliable data.
Cons of Traditional Surveying:
- Time-Consuming: Traditional surveying methods are time-consuming, as they involve manual measurements and data collection.
- Limited Coverage: Traditional surveying is limited in terms of coverage. It may not be practical for large-scale projects where extensive data collection is required.
- Risk of Human Error: Human error can affect the accuracy of measurements, especially in adverse weather conditions or difficult terrains.
Laser Scanning Technology
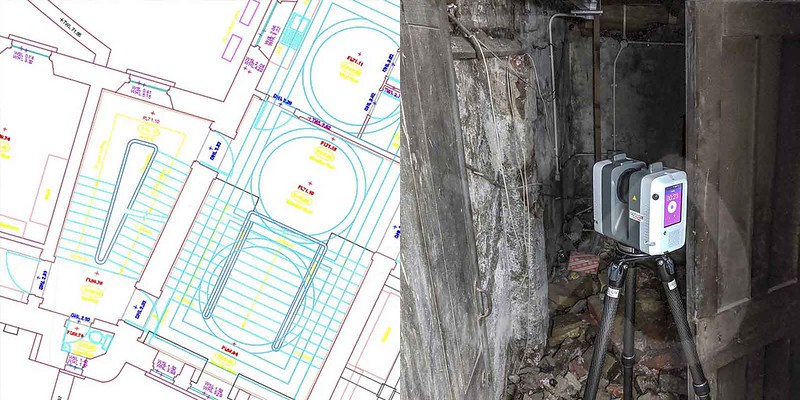
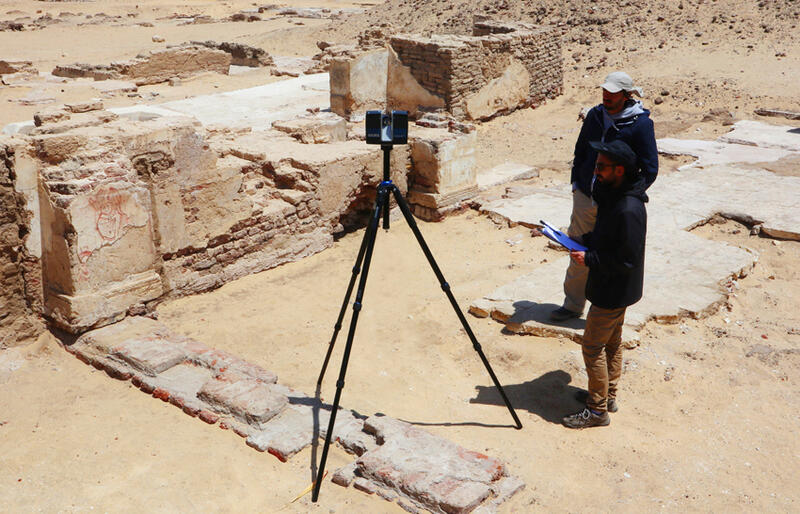
Laser scanning technology, often referred to as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), uses laser pulses to rapidly measure distances and create detailed 3D models of objects, landscapes, or structures. It has gained popularity in recent years for its efficiency and accuracy. Here are the pros and cons of laser scanning technology.
Pros of Laser Scanning:
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser scanning is incredibly fast and efficient. It can collect a vast amount of data in a short amount of time, reducing surveying time significantly.
- High Precision and Accuracy: Laser scanning technology provides extremely accurate measurements, reducing the risk of human error.
- Large Coverage Area: It can cover large areas quickly, making it ideal for large-scale projects like infrastructure development, urban planning, and forestry management.
- Remote Data Collection: Laser scanning can be performed remotely, reducing the need for surveyors to physically access hazardous or hard-to-reach areas.
Cons of Laser Scanning:
- Initial Cost: Acquiring laser scanning equipment and software can be expensive, making it less cost-effective for smaller projects.
- Complex Data Processing: Processing and interpreting the vast amount of data collected through laser scanning can be complex and may require specialized skills.
- Limited Performance in Certain Conditions: Laser scanning may face challenges in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or fog, which can interfere with laser beams.
When to Use Each Approach
The choice between laser scanning and traditional surveying depends on the specific needs of the project and its scale. Here are some guidelines to help you decide:
- Use Laser Scanning When:
- You need rapid data collection for a large area.
- High precision and accuracy are crucial.
- Safety concerns or difficult terrain make remote data collection desirable.
- The budget allows for the initial investment in equipment and software.
- Use Traditional Surveying When:
- You have a smaller-scale project with limited surveying requirements.
- Cost is a significant concern.
- The terrain or environmental conditions are not conducive to laser scanning.
Conclusion
Both laser scanning technology and traditional surveying methods have their own set of strengths and weaknesses. The choice between them should be made based on project requirements, budget constraints, and the desired level of accuracy. Laser scanning has revolutionized the surveying field with its speed and precision, making it an attractive option for many applications. However, traditional surveying methods continue to hold their place, particularly for smaller projects or in situations where laser scanning may not be practical. Understanding the pros and cons of each approach is essential for making informed decisions in the world of land surveying and geospatial data collection.