Archaeology has long been a discipline dedicated to uncovering and preserving our ancient history. Over the years, researchers and archaeologists have employed various techniques and tools to understand our past. One such technology that has revolutionized archaeological research is laser scanning. With its ability to capture highly detailed 3D models of historical sites and artifacts, laser scanning has become an indispensable tool in the archaeologist’s toolkit. Offering unparalleled precision and insight into our ancient heritage.
The Power of Laser Scanning
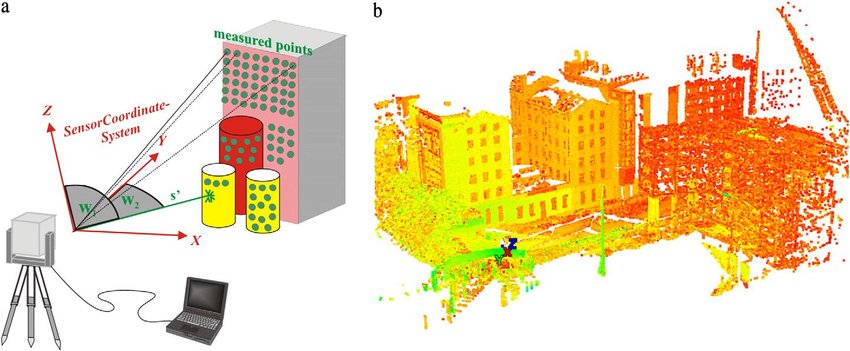
Laser scanning, also known as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), employs laser beams to measure distances and create precise 3D models of objects and environments. In archaeology, this technology has proven to be a game-changer. Allowing researchers to explore, document, and analyze historical sites and artifacts with unprecedented accuracy. Here’s how laser scanning is transforming the field of archaeology:
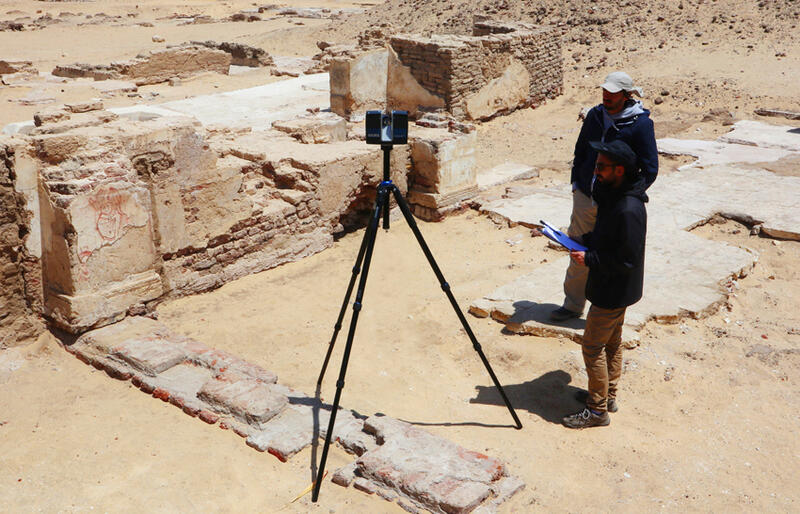
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: Historical sites and artifacts are often fragile and susceptible to damage from environmental factors and human activity. Laser scanning provides a non-invasive method of documenting these treasures without physical contact, ensuring their preservation for future generations.
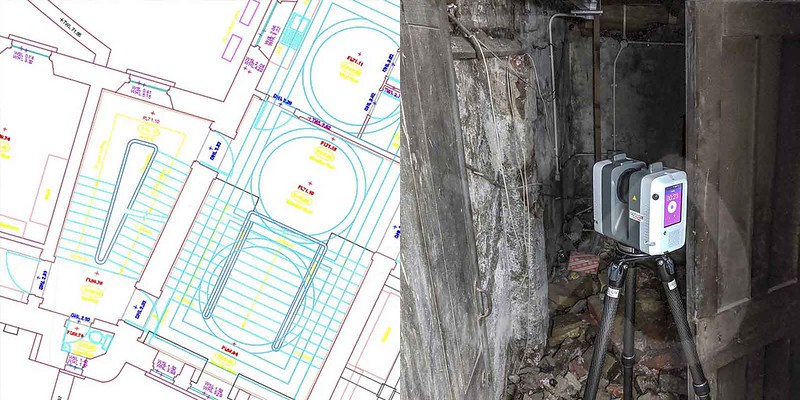
- High Precision Mapping: Laser scanners emit thousands of laser pulses per second, capturing millions of data points in minutes. This data can then be used to create highly detailed 3D models. Allowing archaeologists to map sites and artifacts with an accuracy that was previously unimaginable.
- Rapid Data Collection: Traditional methods of archaeological recording. Such as manual measurements and hand-drawn sketches, can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Laser scanning significantly reduces data collection time, allowing researchers to cover larger areas and gather more comprehensive information quickly.
- Enhanced Visualization: Laser scanning generates 3D models that can be manipulated and explored digitally. This technology enables archaeologists to view historical sites and artifacts from various angles, enhancing their understanding and interpretation of the past.
Applications in Archaeology
Laser scanning is employed in a wide range of archaeological applications, including:
- Site Documentation: Archaeologists use laser scanning to create detailed digital replicas of excavation sites. This not only aids in the accurate documentation of findings but also allows for the visualization of site changes over time.
- Artifact Analysis: Precise 3D models of artifacts, such as pottery, sculptures, and inscriptions, provide insights into their construction techniques. As well as, cultural significance, and historical context. Researchers can zoom in on intricate details and conduct virtual examinations without risking damage to the objects.
- Landscape Analysis: Laser scanning of landscapes, including forests and terrain, helps uncover hidden archaeological features such as ancient roads, settlements, and structures that may not be visible on the surface.
- Heritage Preservation: Laser scanning is instrumental in monitoring and preserving cultural heritage sites threatened by natural disasters, urban development, or climate change. These digital records serve as valuable resources for restoration and reconstruction efforts.
Case Studies
Several remarkable archaeological discoveries and studies have been made possible through laser scanning technology:
- Mayan Cities in Central America: Laser scanning has unveiled the intricate architecture and urban planning of ancient Mayan cities hidden beneath dense vegetation in Central America. This technology has been crucial in uncovering the secrets of Mayan civilization.
- The Hidden Chamber of the Great Pyramid: In 2017, a hidden chamber was discovered within the Great Pyramid of Giza using a combination of laser scanning and thermal imaging. This finding has sparked new discussions about the pyramid’s purpose and construction.
Conclusion
Laser scanning has transformed the field of archaeology, providing researchers with powerful tools to reveal the past with unprecedented precision. Its ability to create highly detailed 3D models of historical sites and artifacts allows for better preservation, visualization, and analysis of our ancient heritage. As technology continues to advance, the future of archaeology looks brighter than ever, promising more astonishing discoveries that will reshape our understanding of history.