Accurate measurements of buildings are essential for a wide range of industries, from architecture and construction to real estate and urban planning. When it comes to measured building surveys, there are two primary methods to choose from: 2D (two-dimensional) and 3D (three-dimensional). Each method has its unique advantages and applications, making it crucial to understand when to use each and how they compare. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between 2D and 3D measured building survey methods and highlight the situations in which each is most appropriate.
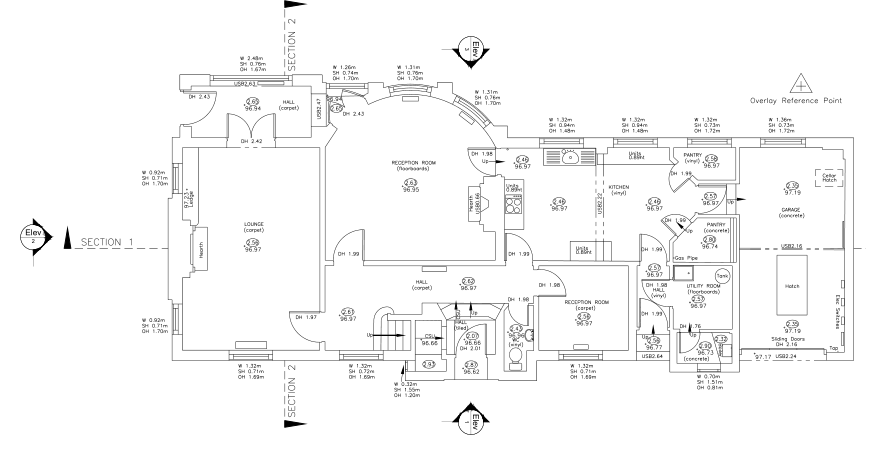
2D Measured Building Surveys
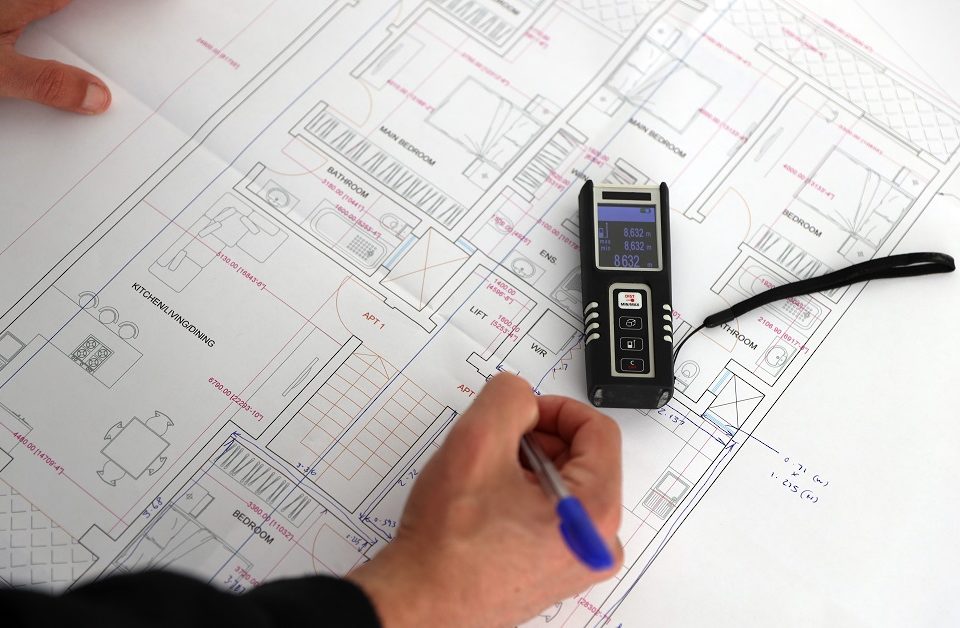
2D measured building surveys are a traditional approach to capturing the dimensions and layout of a building. These surveys are typically done using tools such as tape measures, laser distance meters, and total stations. Here are some key characteristics and advantages of 2D surveys:
- Cost-Effective: 2D surveys are generally more cost-effective than their 3D counterparts, making them a popular choice for smaller projects or those with limited budgets.
- Quick Data Collection: Since 2D surveys focus primarily on capturing linear measurements and floor plans, they are quicker to perform compared to 3D surveys.
- Sufficient for Many Applications: 2D surveys are suitable for tasks like creating floor plans, calculating square footage, and assessing the overall layout of a building. They are commonly used in real estate transactions and property management.
- Ease of Interpretation: The resulting 2D drawings are relatively straightforward to interpret and share with stakeholders, making them ideal for clear communication.
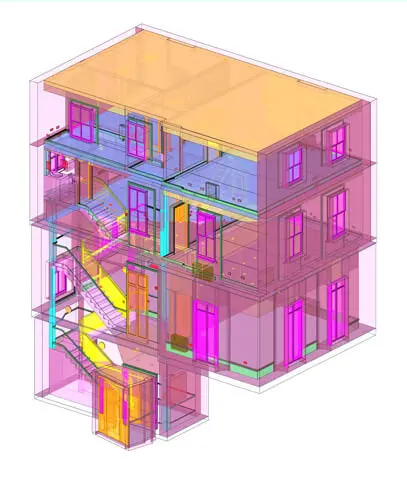
3D Measured Building Surveys
3D measured building surveys provide a more comprehensive view of a building’s geometry by capturing not only lengths and widths but also heights and depths. This method typically employs advanced technologies like 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry. Here are the advantages of 3D surveys:
- Highly Accurate: 3D surveys offer a higher degree of accuracy compared to 2D surveys, especially when dealing with complex architectural elements, irregular shapes, or curved surfaces.
- Comprehensive Data: They provide a complete 3D representation of the building, including structural elements, interior details, and external features. This data is valuable for renovation, preservation, or remodeling projects.
- Efficiency: 3D laser scanning can quickly capture a large volume of data, reducing the time required for fieldwork. It’s particularly beneficial for large or intricate structures.
- Visualization and Analysis: 3D data allows for immersive visualization, analysis, and simulation, enabling architects, engineers, and designers to make more informed decisions.
When to Use Each Method
The choice between 2D and 3D measured building surveys depends on the specific project requirements and objectives:
- 2D Surveys: Choose 2D surveys when you need basic measurements and floor plans for tasks like property appraisal, space planning, or creating building layouts for marketing materials. They are suitable for routine real estate transactions and simple building assessments.
- 3D Surveys: Opt for 3D surveys when you require highly accurate and comprehensive data for complex projects, such as architectural design, structural analysis, historical preservation, or building refurbishment. 3D surveys are invaluable when dealing with intricate building geometries or when precise measurements are critical.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between 2D and 3D measured building survey methods should be based on the specific needs and objectives of your project. While 2D surveys are cost-effective and suitable for many applications, 3D surveys offer superior accuracy and comprehensive data, making them essential for complex architectural, engineering, and design tasks. Ultimately, the right method will ensure that you have the precise measurements and data necessary to successfully complete your project.