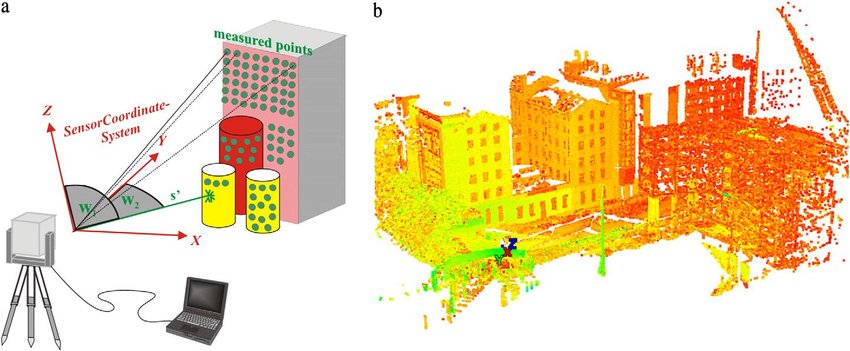
Laser scanning technology has revolutionized various industries, from construction and engineering to archaeology and forestry. It allows us to capture precise three-dimensional data of objects and environments quickly and accurately. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and laser scanning data processing presents its fair share of challenges. In this blog post, we’ll explore some common issues faced during laser scanning data processing and offer tips and solutions to overcome them.
Data Volume Overload
One of the primary challenges in laser scanning data processing is dealing with the enormous amount of data generated during scanning. High-density scans can produce billions of data points, overwhelming even the most powerful computers and software.
Solution:
- Data Filtering: Employ point cloud filtering techniques to reduce the data volume by removing unnecessary points or those with lower quality.
- Decimation: Reduce point cloud density by subsampling points or using voxel-based techniques while preserving critical details.
- Cloud Services: Consider cloud-based processing solutions that can handle large datasets more efficiently.
Registration and Alignment Issues
When conducting multiple scans or using different scanning devices, aligning and registering the point clouds accurately can be a challenging task. Misalignments can result in inaccurate models.
Solution:
- Utilize Targets: Use physical targets or reference points to aid in the alignment process, ensuring that scans are correctly positioned relative to each other.
- Feature-Based Alignment: Some software tools offer feature-based registration, which identifies common features in different scans to improve alignment accuracy.
- Ground Control Points (GCPs): Use ground control points surveyed with high accuracy to ensure precise alignment.
Noise and Artifacts
Laser scanning can be affected by noise and artifacts, such as reflections, shadows, or interference from surrounding objects, which can lead to inaccuracies in the point cloud.
Solution:
- Post-processing Filters: Apply noise removal filters like outlier detection, smoothing, or feature-preserving denoising to clean up the point cloud.
- Quality Control: Regularly inspect the data for anomalies and artifacts during processing, and manually edit or remove problematic points when necessary.
- Proper Scanning Techniques: Ensure proper scanning techniques, including adjusting scanning parameters and avoiding areas with significant interference.
Data Registration Time
Time-consuming data registration and alignment processes can slow down project timelines, especially when dealing with large datasets or multiple scans.
Solution:
- Use Automation: Employ software that offers automated registration algorithms to expedite the alignment process.
- Parallel Processing: Utilize multi-core processors or distributed computing to speed up registration by running multiple processes simultaneously.
- Prioritize Scans: Focus on registering critical scans first to start working with relevant data while the registration process continues in the background.
Data Integration and Visualization
Integrating laser scanning data into existing workflows or software tools can pose compatibility issues, and effectively visualizing the data can be challenging.
Solution:
- Export Formats: Choose export formats that are compatible with your preferred software or utilize software plugins designed for specific applications.
- 3D Visualization: Explore 3D visualization tools and software that allow you to interactively explore and analyze the point cloud data.
- Data Interoperability: Invest in software that supports various data formats and offers integration capabilities with popular CAD and GIS applications.
Conclusion
Laser scanning technology has greatly enhanced our ability to capture detailed 3D data, but processing that data comes with its own set of challenges. By implementing the solutions mentioned above and staying updated on the latest advancements in laser scanning software and hardware, professionals can overcome these challenges and make the most of this powerful technology. With proper processing techniques, laser scanning can continue to revolutionize industries and provide valuable insights into our world.